How Does an Electric Linear Actuator Operate?
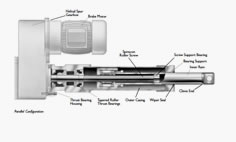
The electric motors rotation drives the primary gear of the gearbox, which through a single or more gear stages turns the gearboxes output shaft (final gear). This rotates in unison with the lead screw, as the lead screw is fixed in place to the gear. When the lead screw rotates the lead nut that mates with the lead screw translates along the screw and so converts rotary motion to linear motion.
The lead nut is fixed to the “ram” or “inner tube” so this item translates with the nut. Note that for linear motion to occur the ram (including lead nut) must be restrained from rotating with the lead screw. This is usually done by fixing the end of the ram via its end connection to the object that needs to be moved. If the object is in free space then the actuators ram needs an anti-rotation device fitted. The outer tube seals the lead screw into the ram which protects the screw from dirt, debris and damage and acts as a lubrication store. In addition the exposed portion of the ram can have a flexible covering attached to provide extra protection (e.g. bellows boot).
